Search Through Time
Find what you knew when, not just what you know now. Bi-temporal search for decision archaeology.
The Problem
The board asks: "Why did you choose React Native over Flutter in Q1?"
You remember the decision. But you remember it through the lens of everything that happened after, the pivot, the performance issues, the rewrite.
You need to answer: What did you know THEN?
"I can search my notes for 'React Native'. But I can't search for 'what I believed in March about React Native'."
The Solution
Nowledge Mem uses bi-temporal search: two dimensions of time that let you find exactly what you're looking for.
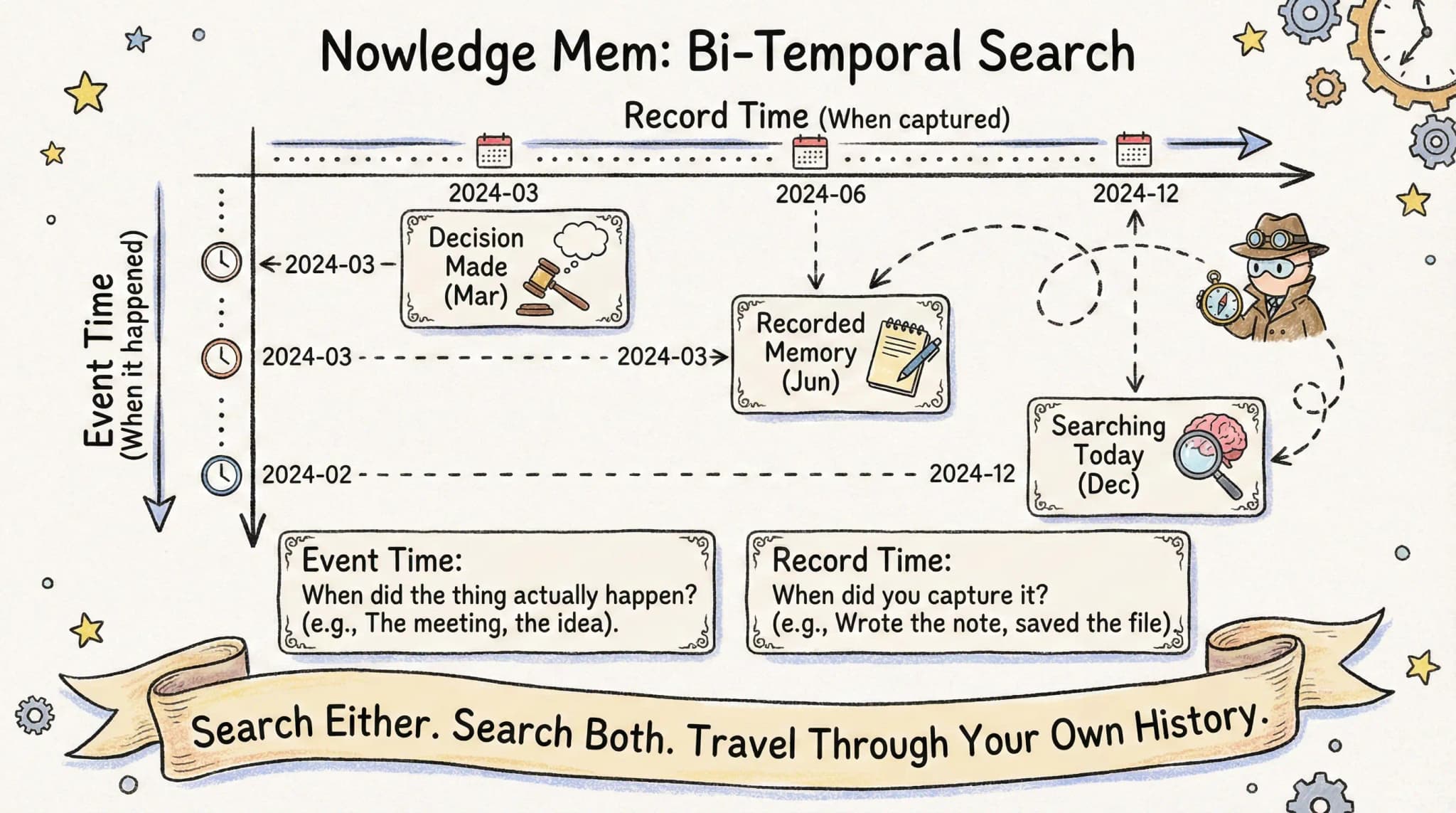
Event Time: When did the thing actually happen? Record Time: When did you capture it?
Search either. Search both. Travel through your own history.
Learn More
Blog: How We Taught Nowledge Mem to Forget.
Documentation about Search & Relevance.
How It Works
Natural Language Queries
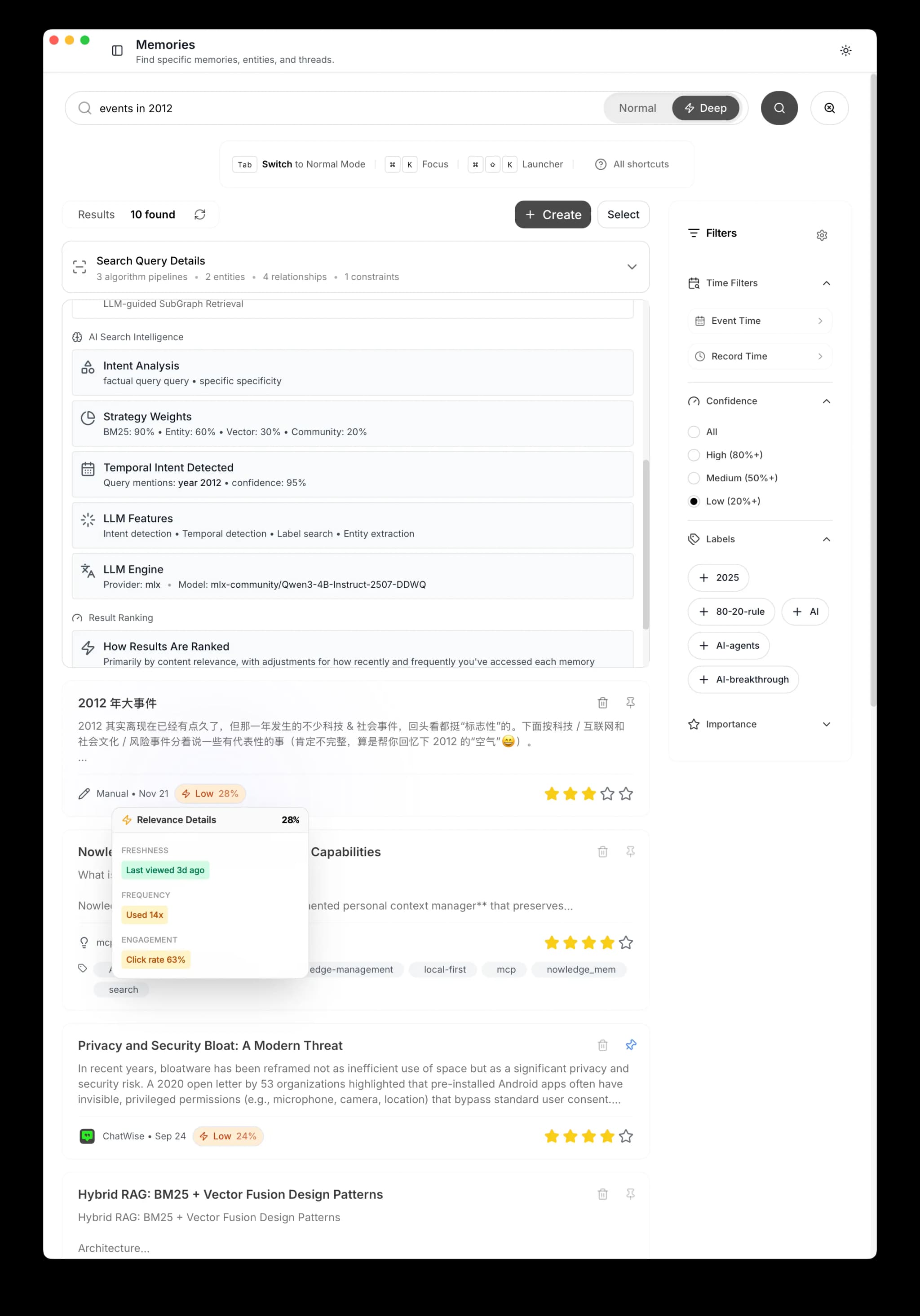
Just search naturally. Nowledge Mem understands temporal intent:
"What did I decide about React Native in Q1 2024?"
The system:
- Detects temporal intent: "Q1 2024"
- Searches memories where the event occurred in that period
- Returns results with original context
No special syntax needed.
Explicit Temporal Filters
For precise control, use the advanced search:
| Filter | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Event Date From | Event happened after | 2024-01-01 |
| Event Date To | Event happened before | 2024-03-31 |
| Record Date From | Written down after | 2024-01-01 |
| Record Date To | Written down before | 2024-12-31 |
Power Query Example:
Event Time: March 2024 Record Time: Any
Returns: "All memories about events from March 2024, regardless of when you recorded them."
Flexible Date Precision
Nowledge Mem handles flexible dates:
- Year: "2024" → Matches anything in 2024
- Month: "2024-03" → Matches March 2024
- Day: "2024-03-15" → Matches that specific day
The system preserves your original precision and displays accordingly.
Real Examples
Board Retrospective
Query: "architecture decisions in Q1 2024"
Result: Original decision memos with Q1 context, before you knew what would break
Compliance Audit
Query: "security policies before the incident"
Result: What policies existed before the breach
Personal Growth
Query: "career goals from 2022"
Result: What you wanted then, compare to where you are now
Project Post-Mortem
Query: "project-x assumptions from kickoff"
Result: Original assumptions that turned out wrong
How Memory Decay Works
Not all memories age equally. Like your brain, Nowledge Mem:
- Prioritizes recent memories by default (30-day half-life)
- Boosts frequently accessed memories (logarithmic scaling)
- Respects importance scores you set (importance floor prevents full decay)
- Learns from your behavior (clicks, dwell time)
This means casual searches surface fresh, relevant results, but temporal searches bypass decay to find exactly what you asked for.
Deep Mode
Temporal intent detection requires Deep Mode search. In Fast Mode, temporal references are matched by keywords only. Enable Deep Mode for queries like "recently working on" or "decisions from last quarter."
See Search & Relevance for the full technical breakdown of how scoring, decay, and temporal matching work.
The Two Times
Understanding the difference is key:
| Question | Which Time? |
|---|---|
| "What did I decide in March?" | Event Time |
| "What did I write last week?" | Record Time |
| "Show recent notes about old events" | Both |
| "What did I know before the pivot?" | Event Time |
Most searches use event time because you're asking about when things happened.
Record time is useful for:
- Finding recent captures
- Reviewing what you've been documenting
- Auditing when knowledge was recorded
Setting Event Time on Memories
When creating memories manually or distilling from threads, you can set the event time:
Open the memory editor
Find the Event Date field
Enter when the event actually happened (not today)
For automatically distilled memories, the AI often infers event time from context.
Pro Tip
For decisions, always set the event time to when you made the decision, not when you recorded it. Your future self will thank you.
Knowledge Graph + Time
Your graph view respects temporal filters too.
Set Event Time to "March 2024" and see:
- Only entities that existed then
- Only connections that were known then
- The state of your knowledge at that moment
Watch your understanding evolve over time.
Why This Matters
Traditional search finds content.
Temporal search finds context.
"We didn't make a bad decision. We made the best decision with what we knew. Here's the proof."
Your memories aren't just searchable. They're time-stamped, version-controlled, and historically accurate.
Because sometimes the most important question isn't what or where.
It's when.
Next Steps
- Give Your AI a Memory → Share context across tools
- See Your Expertise → Visualize your knowledge
- Advanced Features → Knowledge graph capabilities